The killing fields of Libya's Tarhuna
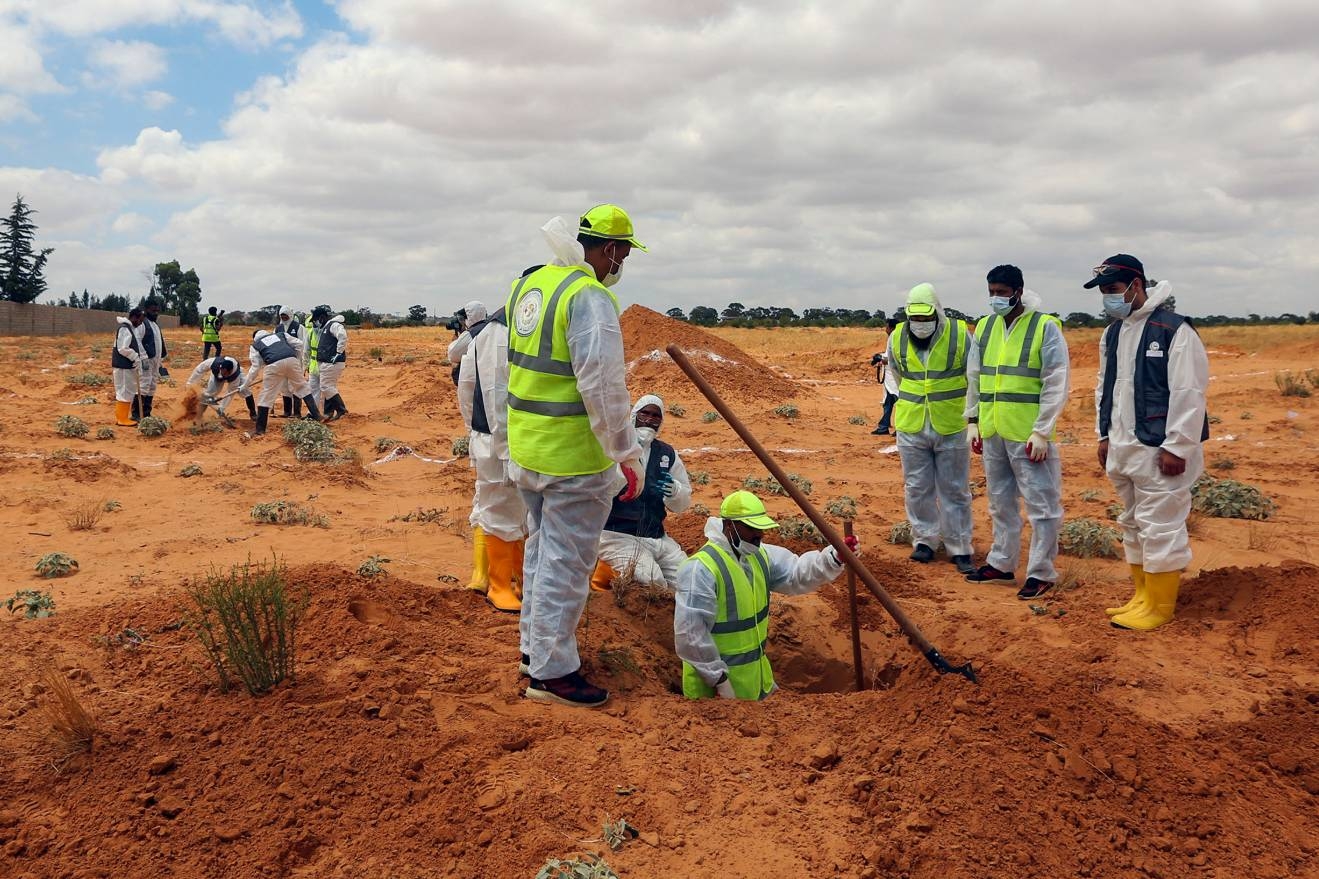
TARHUNA, Libya - At the Haruda family’s farm, agricultural labourers have been replaced with forensic teams, their bright white protective suits silhouetted against dusty, rust-coloured soil. Areas for excavation have been marked out in chalk, like macabre football pitches. Little triangular flags beside shallow potholes indicate each place bodies have been found.
Tarhuna, a rural town 60km southeast of Tripoli, where olive trees stripe low hills rising out of Libya’s coastal plain, is searching for its dead.
Almost 80 corpses have been pulled from the ground in two and a half months, 56 in the Haruda farm alone. Officials believe three times that number could still lie under Tarhuna’s fields and orchards.
“We still have a lot to dig. Just 20 percent of this area has been excavated,” says Mohammed Ali al-Kosher, the town’s mayor.
New MEE newsletter: Jerusalem Dispatch
Sign up to get the latest insights and analysis on Israel-Palestine, alongside Turkey Unpacked and other MEE newsletters
“People of all backgrounds were killed and buried here, including a 10-year-old child. We’re finding new bodies every day. One man was even buried with his car, his hands tied to the steering wheel.”
'People of all backgrounds were killed and buried here, including a 10-year-old child. We’re finding new bodies every day'
- Mohammed Ali al-Kosher, mayor
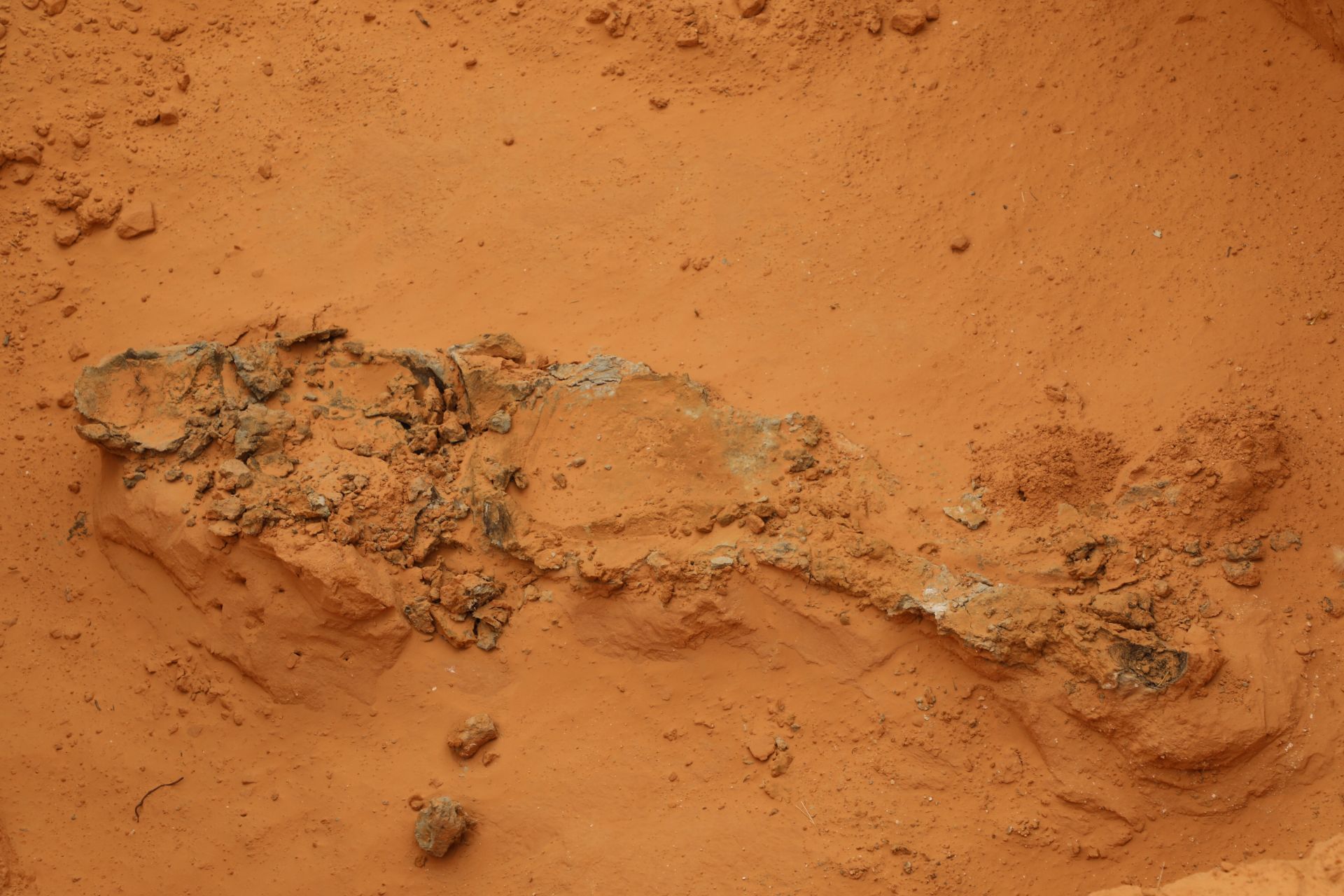
The teams searching for corpses look for tell-tale signs – a chemical change in the soil, mounds of earth piled up nearby, lingering smells.
In two graves from which bodies were retrieved the day before, blood and decomposed tissue has fossilised the victims’ outline in the earth. Forensic teams sieve the soil, finding fragments of bone and clumps of hair. The stench remains.
Tarhuna is traumatised, with emotional scars running far deeper than the crevices carved into the ground in the search for victims.
For 14 months this town of 40,000, whose fertile lands were once prized by Italian colonisers and favoured by Muammar Gaddafi, was transformed into a military base from which eastern commander Khalifa Haftar launched his ill-fated assault on Tripoli.
Hundreds of civilians were killed in the fighting around the Libyan capital between April 2019 and June 2020, but in Tarhuna people were disappeared for the smallest of infractions or suspicions of allegiance.
When Tarhuna was taken on 5 June by forces loyal to the Tripoli-based Government of National Accord (GNA), they discovered 106 bodies stacked up in the local hospital’s morgue. Quickly, authorities realised the town held several mass graves, too. The Haruda farm is the largest of eight found so far, with search teams believing that number could rise to 12.
Kosher, who the GNA placed in charge of a temporary steering municipality after taking the town, says it will take at least a year to excavate all the suspected sites, particularly without better equipment and international support. UN Secretary-General Antonio Guterres has called for a “transparent investigation”, but so far little assistance has been forthcoming.
“From a religious point of view, this is not a decent burial. This is what Daesh does, these are the actions of people who desecrate Islam,” Kosher says, staring into a pit where 11 bodies were recently retrieved.
“The killings were a message: even opposing the fighting in Tripoli can lead to death. This was all done with the blessing of Haftar and his allies.”
Tarhuna: Haftar's launchpad
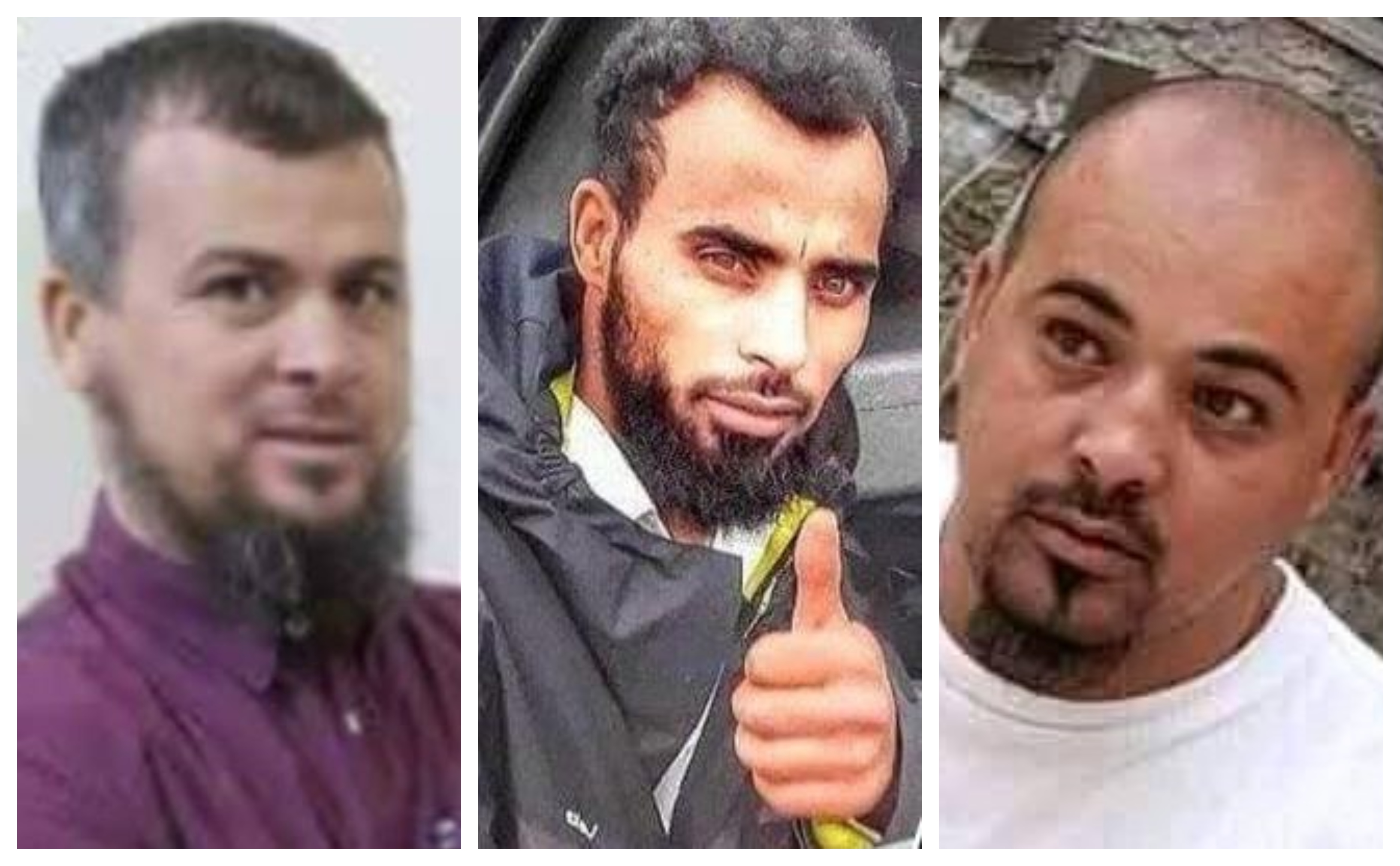
For five years, Tarhuna was ruled by a family of bloodthirsty brothers, the Kanis, and their eponymous Kaniyat militia, also known as the 7th Brigade.
Essentially mobsters, who in the tumult of post-Gaddafi Libya carved out a fiefdom in this western town, the Kani family momentarily gained geopolitical significance early last year, when Haftar sought to use their territory as a launchpad for his assault on the Libyan capital.
Haftar, a UAE, Egypt and Russia-backed warlord who commands a collection of militias known as the Libyan National Army (LNA), had long eyed Tripoli.
To his surprise, however, armed groups from Tripoli and Misrata rallied around the UN-recognised GNA with potency, and his offensive bogged down in the capital’s outskirts.
As the conflict progressed, Turkey poured drones, equipment and Syrian mercenaries into Libya, swinging the fighting decisively in the GNA’s favour until the LNA melted away in June this year.
During those 14 months, when Tarhuna was awash with LNA battalions and foreign mercenaries, Haftar’s Kaniyat allies became increasingly suspicious of the population they repressed, with disastrous consequences for the town’s residents.
Paranoia and conflict industrialised the Kanis’ murderous tendencies. Crackdowns on dissent - both real and imagined - became daily occurrences. Whole families disappeared at a whim.
Today, mementos of murder can be found in almost every neighbourhood, every farm.
Near a construction site yet to be probed for bodies lies a fridge, its inside caked in dried blood.
Elsewhere, a battered white car riddled with bulletholes has ploughed into some trees. To the side, two black shoes, a pair of high heels and a knot of hair in the mud are all that remain of its passengers.
Tarhuna’s now-bustling junctions were once the scenes of Kaniyat checkpoints, where LNA militiamen arbitrarily pulled men out of their cars for perceived infractions, never to be seen again.
One road by an open field, known as the “triangle of death”, was a favoured place for summary executions. Neighbourhoods on three sides could witness the killings.
Most of those found in the hospital have been identified, including children. But of those being pulled from the ground, just a couple, including a man in his 60s found dumped in a well, have been named.
The sheer volume of horror stories Tarhunis have to share is overwhelming: casual conversation can reveal a resident is missing several brothers, cousins or uncles. Hundreds of children now have no fathers.
There is palpable relief that the LNA and Kaniyat have gone, but suspicion - both of fellow Tarhunis and state institutions in general - is widespread.
According to the Tripoli-based General Authority of Search and Identification of Missing Persons, some 270 people are reported lost in Tarhuna. But D Mohamad Ziltny, its international cooperation manager, estimates 150 more have yet to be reported, with fear of reprisals still hanging over the town.
Though the Kanis fled in June, their menace remains.
Residents complain of phone calls from the brothers, threatening retribution if their crimes are exposed and promising a return from exile in Libya’s Haftar-held east.
Rule of the Kani brothers
At first glance, Mohammed al-Kani does not resemble a warlord. The eldest, quietest, best educated of the seven brothers, he was the only Kani to hold down relatively well-paying jobs, in the security services and the state oil company.
Behind that calm veneer, however, was a ruthlessness and unpredictability. Supplicants could be as likely killed as have their requests accepted.
“He was the thinker. He came to be like a sheikh. Like Al Pacino in the Godfather, Mohammed was always thinking, as opposed to necessarily getting his hands dirty,” Jalel Harchaoui, an analyst and expert on Tarhuna, tells MEE.
Tarhuna timeline: 2011 - 2020
+ Show - HideHow a town of 40,000 people became pivotal in the Libyan conflict:
2011: A Nato-backed uprising against Muammar Gaddafi topples the longtime autocrat, who is killed in October.
2012: Ali al-Kani, the only Kani brother to rebel against Gaddafi, is murdered on the road to Tajoura by a group of men, including some from the rival Naaja family. Mohammed al-Kani, who is in Saudi Arabia for Hajj, orders no action to be taken until he is back.
Mohammed’s return to Tarhuna is followed by a string of murders and lynchings. One man suspected of killing his brother is paraded in a central square. The reprisals are the start of the Kanis’ ascent.
2014: Libya is divided by a new civil war. The Kani clan back the Tripoli-based Libya Dawn administration and reject Haftar’s offensive against Islamists and militants in Benghazi.
2015: The Kanis have full control over Tarhuna. They now control a force of 4,000 men known as the Kaniyat, or 7th Brigade, absorbing local security services.
2017: Millions of migrants and refugees passing through Libya en route to Europe prompt the Kani to set up an anti-smuggling operation.
2018: The Kanis agree deals with rivals in Misrata and Zintan, before launching an assault on Tripoli. The Kaniyat attacks the Libyan capital, claiming it is doing so to stop corruption and embezzlement, although in reality it wants funds and influence. To the Kanis’ chagrin, the Mistrans largely stay out of the conflict: the assault ultimately backfires and costs more than 100 deaths.
2019: Haftar allies with the Kanis: the Kaniyat become the 9th Brigade of his Libyan National Army (LNA). In April, the LNA assault Tripoli from Tarhuna and Gharyan. Despite believing the conflict would last weeks, the offensive drags on.
In September Mohsen al-Kani is killed alongside younger brother Abdul Azim. The Government of National Accord (GNA) counterattacks Tarhuna in October and December, exposing LNA weaknesses. In retaliation the Kaniyat take out reprisals on the Tarhuna's residents.
2020: In late May the LNA is struggling to hold its positions around Tripoli, and pro-Haftar Wagner Group Russian mercenaries retreat from the frontline. As LNA fighters begin to retreat, the Kaniyat fire on them in an attempt to stop the collapse.
GNA forces capture Tarhuna in early June. The Kanis and Kaniyat flee east.
“The other brothers were more into physical action, whilst Mohammed was the brains behind the operation. If you walk away from a conversation with Mohammed, you don’t walk away with the impression that you just spoke with a gangster, with hundreds of corpses beneath his feet.”
Beside him was Mohsen, a headstrong military man who headed Kaniyat assaults on Tripoli, both during Haftar’s offensive and in summer 2018, when the Kanis attacked the capital in a quarrel over state revenues.
Demanding, independent and contemptuous of his LNA colleagues, Mohsen proved a headache for Haftar, taking the warlord’s weapons but refusing his orders.
That tension has contributed to suggestions that his September 2019 killing, the circumstances around which remain murky, was facilitated in part by LNA elements. His death, alongside a younger brother, was met among the Kaniyat with a howl of rage that saw dozens of detainees executed in retribution.
The man leading the crackdown at home was Abdul-Rahim al-Kani, whose role in Tarhuna is likened by Hachoui as heading the mukhabarat, or secret police.
A shaven-headed enforcer, Abdul-Rahim’s task was to maintain the Kanis’ increasingly unsure position in Tarhuna as the Tripoli offensive dragged on.
The Kanis drew their wealth from multiple sources: a cement factory, agricultural assets, skimming money transferred by Tripoli to the municipality. They also enforced a protection racket, practiced extortion and ransomed people seized almost at random.
But like the mafia they were, the Kani also played the role of benefactors, handing out favours and endowments to Tarhuna residents struggling in Libya’s collapsed economy.
Between 2015 and the moment it joined the LNA, the Kaniyat held a firm grip on Tarhuna, wrested violently from its rivals and maintained through occasional purges. Until Haftar’s offensive, its strict rule provided the town with a modicum of stability.
“If you’re in Libya in 2015, you look around and it’s just a nightmare everywhere you look. Tripoli was very dangerous, you had Daesh in Sirte and Daesh in Sabratha, corpses on the beaches of Zuwara, it was just horrible everywhere,” Harchaoui says.
“And Tarhuna was very pleasant. It was quiet, it was very safe - you know, how North Korea is very safe.”
The Kanis bet that backing Haftar would only increase their wealth and status. It was a bet they lost.
'It could not end well'
By 13 November 2019, things were not going well for Haftar or the Kanis.
Mohsen was dead, Gharyan, the LNA’s other supply line to the Tripoli front, had been retaken by the GNA, and a daring attack on Tarhuna’s al-Dawoon neighbourhood the month before had shown that the Kaniyat were vulnerable.
Disappearances were increasing, so when Ahmed Abdul Moler Saed Abdul Hafid received an anxious call from his brother that evening, he feared the worst.
“The call was short. All he managed to say was ‘I’ve been stopped in my car’ before the line went dead. Immediately I realised the Kanis had him, and knew it would not end well.”
Abdul Hafid, 39, had previous run-ins with the Kanis. Two years earlier they had extorted him and forced him to buy camels at an exorbitant price. But he’d always coped with their demands well. This time he assumed money could get him out of trouble again.
“At around 12am I went to my family home, found the rest of my brothers and told them to gather as much money as they could for ransom.”
'I lost five brothers to the Kanis, and a friend who was more than a brother'
- Ahmed Abdul Moler Saed Abdul Hafid
From there he went home, turned off all the lights and lay down with his wife, pretending no one was home. After a sleepless night, he heard more chilling news. The rest of his brothers had been taken.
Abdul Hafid knew he had to get out, and with the help of a friend, who would then be seized for assisting him, crept out of Tarhuna and walked 80 km north to the town of Tajoura.
“Everything they did came out of nowhere. You cannot even measure their criminal behaviour, there was no limit,” Abdul Hafid says, sitting bolt upright in his family’s reception room, the memories leaving his face pallid and wrought.
“I lost five brothers to the Kanis, and a friend who was more than a brother,” he says. “There was no obvious reason for their arrest. We are businessmen, not al-Qaeda or the Muslim Brotherhood.”
Like many other Tarhunis forced to flee, Abdul Hafid rushed back to his hometown the day the Kaniyat left. “When I walked through the door of my family’s home my mother fainted, then fainted again. I shouted ‘where are my brothers, where are my brothers?’ I knew something was deeply wrong.”
The prisons were open, but there was no sign of his siblings.
“The Kanis are not people, they are savages. We heard reports people may have been fed to lions.”
Tarhuna's torture prisons
Rumours of the torture prison the Kaniyat had created in a local agricultural testing centre had spread for weeks before they left Tarhuna, and the Kanis knew it.
In December, they had erected earth berm fortifications on two sides, fearing reprisal attacks from the families of those detained there.
When GNA forces eventually took the complex, they found seven, square-metre compartments, each of which was just large enough to accommodate a crouched man. On the counter above them lay mounds of ash from fires the Kaniyat used to turn the tiny cells into ovens.
“When we discovered this place we found one man still crouched inside an oven - he was alive but in a terrible state. He wouldn’t come out, he thought we were the Kaniyat playing a trick on him,” says Kosher.
'Sometimes the prisoners would come back, sometimes they had been killed'
- Ali Asaid Abu Zweid, former prisoner
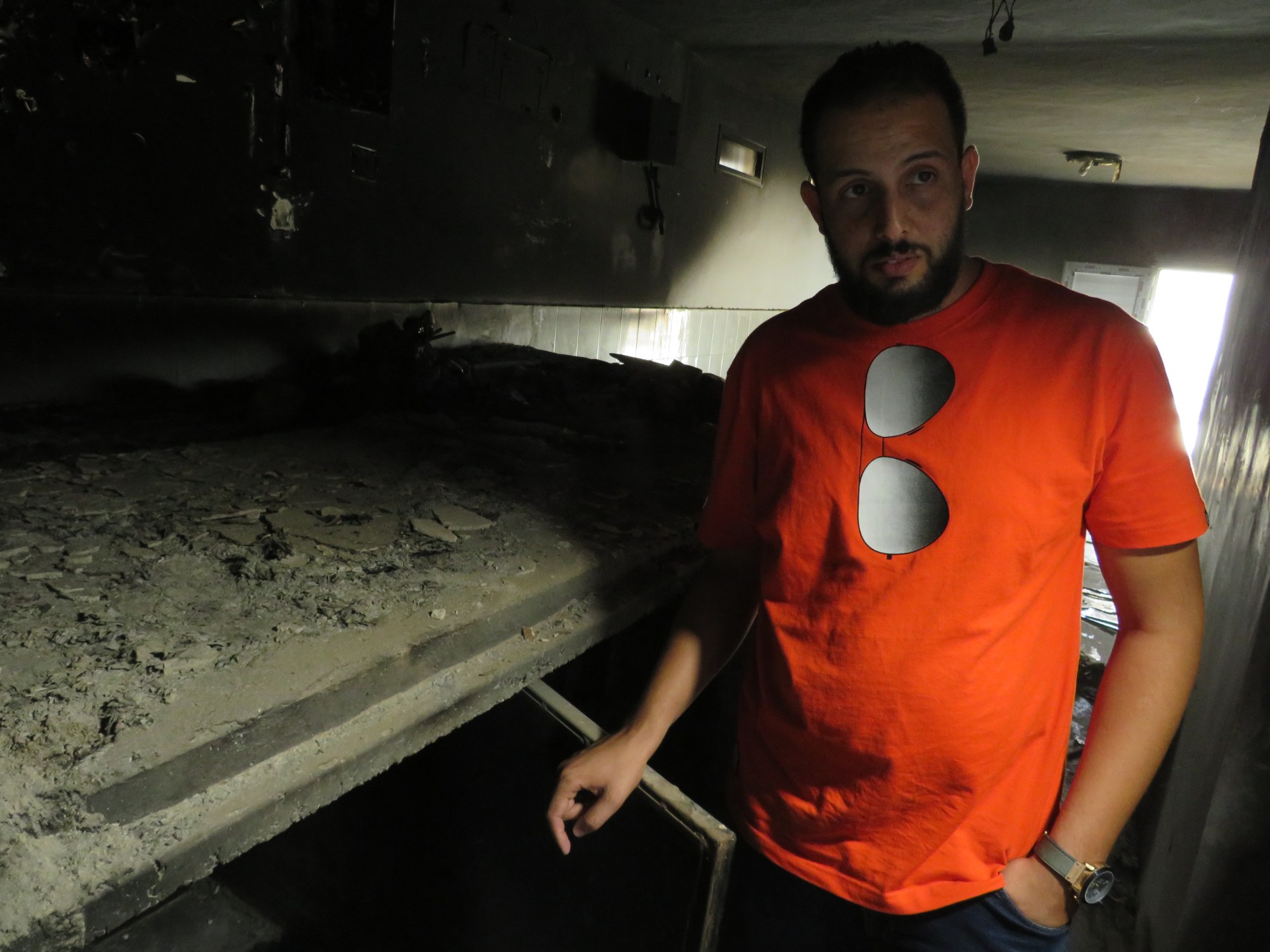
Much of the facility is now blackened and charred, following fires Tarhunis lit in anguish when they realised their relatives couldn’t be found. But cardboard mattresses and fingerprints smeared down cell walls hint at its former use.
Ali Asaid Abu Zweid was held in one of these cells for 45 days, during which he barely spoke a word to the detainees to his left and right.
“We remained almost completely silent while held there, because no one thought it would be safe to talk to each other,” he says.
It’s unclear exactly why he was seized and held here, though Abu Zweid suspects it’s because he’d fought alongside pro-GNA Misratans against the Islamic State group in Sirte in 2015, but refused to take up arms against them in Tripoli.
He lost 30kg over a month and a half. “When they took someone off to be interrogated you’d hear gunshots,” he recalls, standing outside his former cell. “Sometimes the prisoners would come back, sometimes they had been killed.
“Occasionally they’d light fires over the ovens – it depended on our guards’ mood.”
Further into town, the Kaniyat used a former interior ministry security branch as a detention facility, where they held the majority of prisoners. Scores were confined here at once, crammed into half-a-dozen rooms strewn with plastic bottles used as toilets.
In one cell, brightly coloured children’s shoes are scattered over the floor.
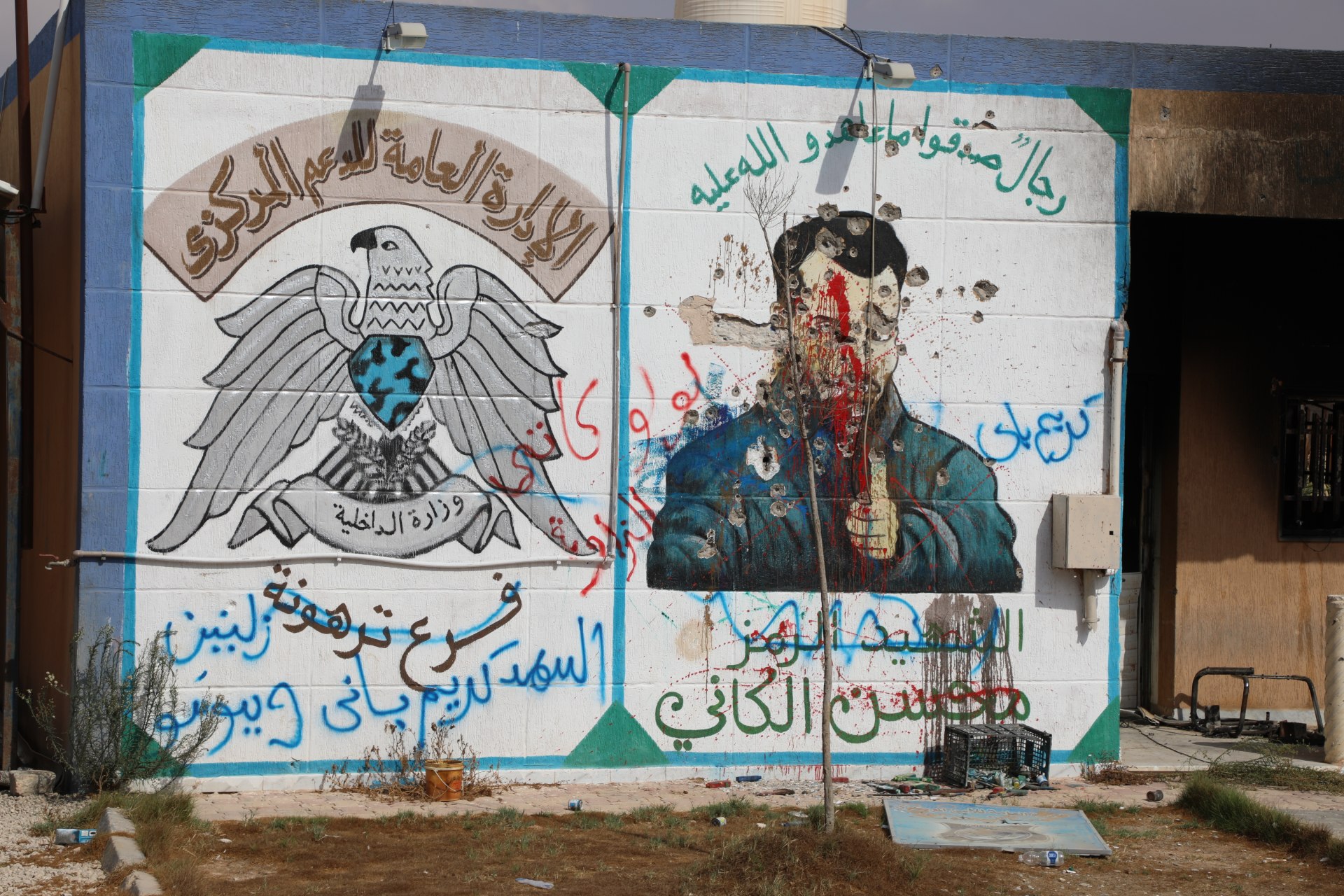
Like the agricultural centre, the majority of people held here are still missing. Left behind by the Kaniyat instead are a falanga instrument to beat detainees’ feet and a mural of Mohsen al-Kani, staring out into the courtyard and giving the thumbs up.
A few names of people and places have been etched into the heavy metal doors that locked people in, along with dates. Officials investigating the disappearances believe these signify days when events happened, including purges. Some dates have several marks scored beside them, possibly marking the number of people killed at that time.
The cost of the Kanis
Tarhunis are still counting the cost to their town’s social fabric. The Kanis turned cousin against cousin. Those who managed to flee the town say they have been subject to vicious rumours.
But for women like Gazalla Ali Awness, who watched the Kani snatch seven of her sons, just providing for the dependents they left behind is a struggle. She now has around 40 grandchildren to support.
'I don’t want money or food, I just want my sons, give me just one'
- Gazalla Ali Awness, Tarhuna
“The oldest man we have left is this one, he is 13,” she says, running her fingers through a boy’s thick black hair.
Surrounded by children, Awness looks up at the sky and flings out her arms, desperation and loss cracking her voice. “I don’t want money or food, I just want my sons, give me just one.”
Without a body, moving on mentally and emotionally can be near impossible. But economically, too. Under conservative Islamic tradition, a woman can’t remarry until her husband is confirmed dead. With so many missing, and so many bodies yet to be identified, several of Tarhuna’s women are unable to turn a page or secure support from a new breadwinner.
“Now I have to do everything myself, and provide everything for my grandchildren and their mothers,” Awness says.
Though it has been weeks since the Kaniyat last stalked these streets, nerves are frayed.
Residents told MEE they avoid reporting relatives and friends who are missing because people they saw as complicit with the Kanis’ rule can still be seen around the municipal office.
Just the sight of men carrying weapons is too much for children of the Jaballah family, who burst into tears and hide every time the security services roll past their home.
Tarek Ali al-Jaballah was shot on the street in front of his young son in December. The next day, the Kaniyat rounded up 10 more members of the family. “Leave no men,” Sabri al-Gharb, a former Gaddafi loyalist leading the raid, is reported to have said.
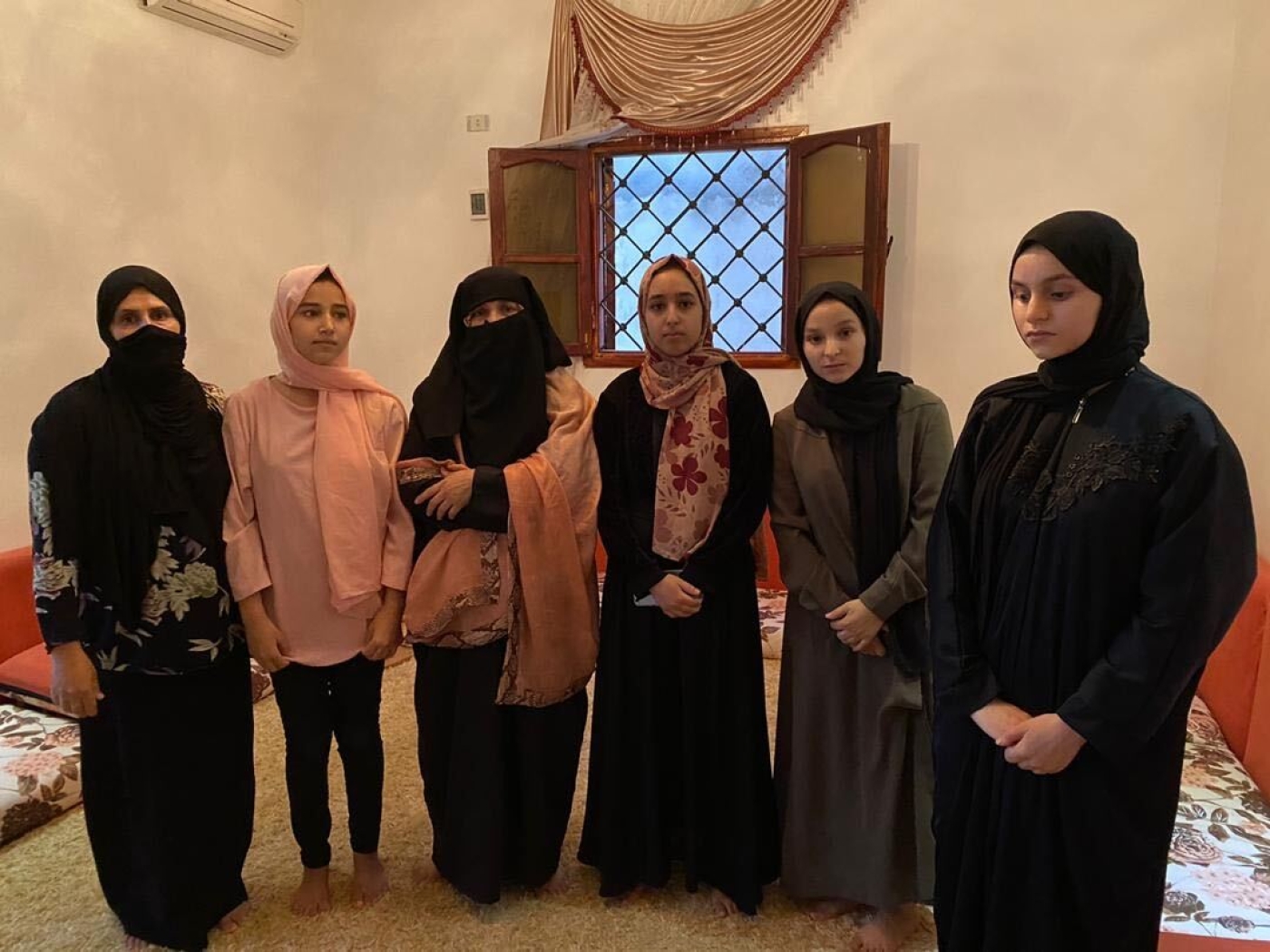
“I have lost my husband, four brothers, one uncle and four cousins,” Rabia al-Jaballah says, fighting back tears. “I’m still frightened.”
“My brother was shot,” a teenage girl sitting behind her says.
“My father is missing,” another adds. “I miss him. I have dreams, I wanted to become a doctor, but I can’t do this without him.”
Reprisals in Tarhuna
The days that followed the GNA forces taking Tarhuna were pandemonium, with looting, arson and arrests recorded in several victorious fighters’ social media posts.
Lions kept by Mohsen and suspected to be fed with his victims were shot dead at his abandoned home.
Sources in the town told MEE at the time that extrajudicial killings were carried out. Kosher insists just a couple of people were killed in an inter-family dispute, although sources in western Libya have quietly acknowledged that reprisal killings could have reached the dozens.
Pro-Haftar media has seized on this narrative, ignoring the mass graves or blaming them on Syrian mercenaries while disassociating the LNA from the Kaniyat.
'I’m sure that Haftar was not receiving a text message every time a kid was killed, of course not, but that doesn’t take away from the sense of responsibility and complicity'
- Jalel Harchaoui, analyst
Yet the Kanis, the Kaniyat fighters and their families – totalling around 15,000 people overall – are still hosted by Haftar in east Libya. Abdul-Rahim al-Kani has married into a prominent tribal family in the eastern city of Ajdabiya, whose fighters fought alongside the Kaniyat in Tripoli, and has even reportedly travelled to Germany for medical treatment.
The Kaniyat presence in the east is not particularly welcome, however. Mahmoud al-Werfalli, an LNA commander wanted by the International Criminal Court for war crimes, reportedly refused to allow the Kanis to settle in Haftar’s capital Benghazi.
“They’re not accepted there, they’re considered radioactive,” Harchaoui, the analyst, says. “If you go to war together, and then the war turns out to be a catastrophe on every level, then you’re going to hate each other.”
That said, during the Tripoli offensive, Haftar and his backers, including the UAE media, talked up the Kaniyat and stressed its legitimacy as part of the LNA. At one stage, the Kanis’ militia was combined with veteran LNA unit the 22nd Brigade to create the 9th Brigade, consolidating its place in Haftar’s ranks cosmetically and practically.
“I’m sure that Haftar was not receiving a text message every time a kid was killed, of course not, but that doesn’t take away from the sense of responsibility and complicity,” Harchaoui says.
“You can call it indirect, if you want. You can call it opaque, if you want. But it’s still complicity with an actor that everybody knew committed these atrocities.”
Fatou Bensouda, the ICC’s prosecutor, has said the discovery of men, women and children buried in Tarhuna’s mass graves “may constitute evidence of war crimes or crimes against humanity”.
The ICC prosecutor’s office told MEE it is “following up on this matter in particular with the competent Libyan authorities, in accordance with the principle of complementarity, to ensure that these mass graves are investigated”.
The LNA, meanwhile, described the mass graves as "crimes against humanity".
"They were committed before the army went to Tripoli when the Kaniyat militia was affiliated with the forces of the Government of National Accord," LNA spokesman Major General Ahmed al-Mismari told MEE.
Mismari would not commit to sending any wanted people in LNA territory to The Hague if requested by the ICC, and did not respond to questions about whether Haftar's forces took responsibility for crimes committed by militias fighting under their banner.
In Tarhuna, there's a growing realisation that the remains of all the town's missing can only be recovered if the Kaniyat reveal their whereabouts. "Those in the east know where the bodies are buried,” says Kosher.
And for Tarhuni survivors like Rabia al-Jallabah, the onus is on Haftar to recognise the murders committed under his watch and stop giving shelter to those responsible.
“We want the UN to put pressure on Haftar. All we want is for the criminals who escaped to the east to be brought to justice," she says. "They will do in the east what they did here.”
This article is available in French on Middle East Eye French edition.
Middle East Eye delivers independent and unrivalled coverage and analysis of the Middle East, North Africa and beyond. To learn more about republishing this content and the associated fees, please fill out this form. More about MEE can be found here.