Autopsy shows chemical weapons used in Syria attack: Turkey
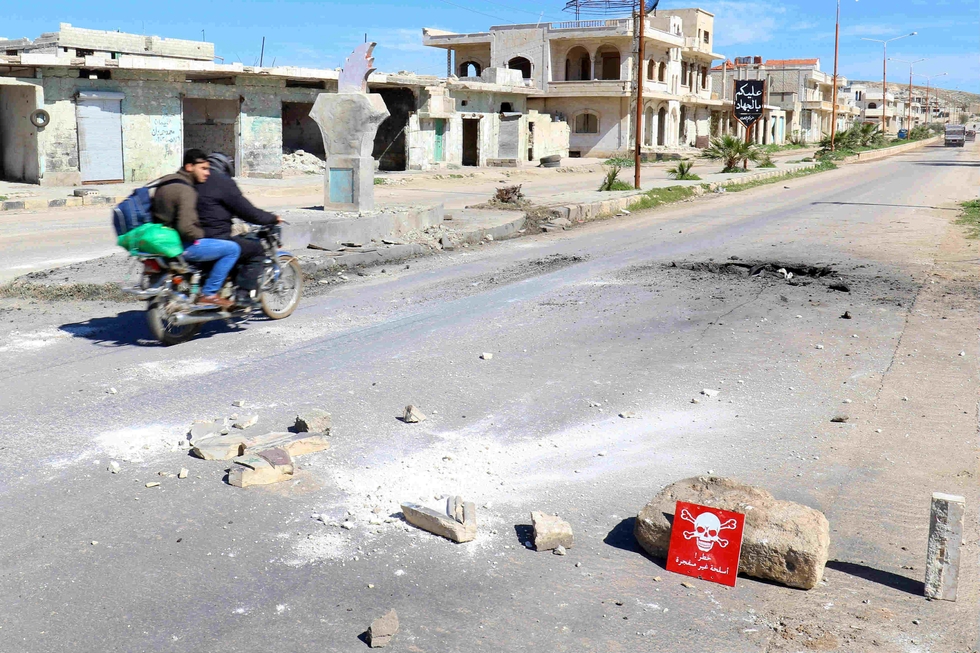

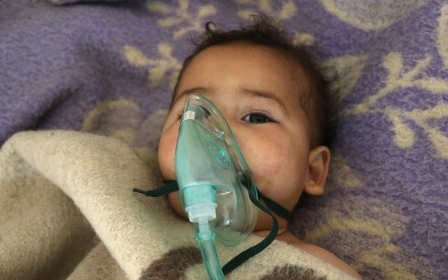
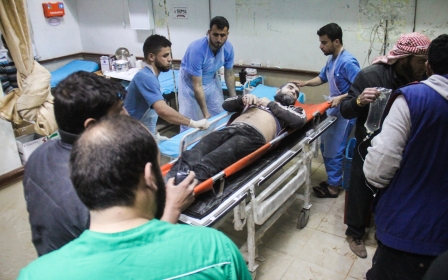
Autopsy results have revealed that chemical weapons, and possibly Sarinn were used in an attack which killed at least 70 people in Syria's Idlib province, Turkey said Thursday.
Turkish Justice Minister Bekir Bozdag told reporters that "Autopsies were carried out on three of the bodies after they were brought from Idlib. The results of the autopsy confirms that chemical weapons were used," quoted by state-run Anadolu news agency.
"This scientific investigation also confirms that Assad used chemical weapons," Bozdag added, without giving further details.
Thirty-two victims of Tuesday's attack have been brought to Turkey and three have subsequently died.
The Turkish Health Ministry later said the substance was possibly Sarin, which was also used in the deadly 2013 Ghouta chemical attack, and reserves of which the Syrian government said it had given up.
Bozdag said autopsies were conducted with the "participation" of officials from the World Health Organization (WHO) in the southern province of Adana together with officials from Organisation for the Prohibition of Chemical Weapons (OPCW).
But WHO immediately countered Bozdag's claims that it was involved in the postmortem, saying the organisation did not conduct autopsies, adding: "It is not our mandate."
WHO spokesman Tarik Jasarevic told AFP in Geneva that "a WHO person was there at the time of the autopsy but had no role in the autopsy or investigation".
He also stressed that no samples or swabs had been taken by WHO despite claims by the Adana prosecutor that "examples" had been sent to the organisation and the OPCW.
In a statement, the prosecutor, quoted by Anadolu said: "For analysis, examples were taken and sent to (medical institutions). Separately, following requests from the World Health Organization and the United Nations Organisation for the Prohibition of Chemical Weapons, examples were given (to them)."
Middle East Eye propose une couverture et une analyse indépendantes et incomparables du Moyen-Orient, de l’Afrique du Nord et d’autres régions du monde. Pour en savoir plus sur la reprise de ce contenu et les frais qui s’appliquent, veuillez remplir ce formulaire [en anglais]. Pour en savoir plus sur MEE, cliquez ici [en anglais].