Diggers, denial and despair: The macabre story of the Srebrenica cover-up
TUZLA, Bosnia-Herzegovina - There is no ventilation in the room where they keep the bodies. There is no central heating in the room the forensics team work in. The cleaners were laid off long ago because there is no money to pay them. The plumbing in one of the lavatories is bust. The rent has gone unpaid for 12 months. The building is a dreary industrial unit with uncleaned windows and broken shutters.
Welcome to the International Commission on Missing Persons in Tuzla where earnest and stretched forensic anthropologists try to identify the victims of the Srebrenica genocide.
'He said he wanted to kill me, he chased us across the field cursing my dead children ... The police did nothing; this is Srpska now'
We had blithely assumed that the international community - and the governments of both Bosnia-Herzegovina and Serbia - would have ensured that the organisation working to find mass graves, painstakingly identify the bodies and then inform the families, would be adequately funded until the very last victim was found. We were wrong: "We wanted to get sniffer dogs to find the remaining graves," the only staff member in the building told us, "but we couldn't afford it."
The rundown building is a perfect metaphor for a genocide that is forgotten by many, ignored by others, and completely denied by many of those most closely involved.
Dragana Vucetic, a 36-year-old Serb, is the director of the centre. A forensic anthropologist by training, she was a child in Belgrade during the terrible civil wars that ripped apart the Balkans in the 1990s.
Dragana joined the International Commission on Missing Persons straight after university and has worked tirelessly in the 13 years since.
Thanks to modern DNA techniques, the International Commission on Missing Persons has been able to identify him, even though much of his body is missing.
His family have been informed, and they are now ready to bury the remains. Many families, however, delay for years, waiting for more bones to be found. The reason for the majority of these delays is macabre.
Mass graves dispersed with diggers
As Serbian paramilitaries found themselves hounded by international investigators intent on bringing the murderers to justice, they would carve up the mass graves at night with diggers, move the soil and bones to secondary sites, and then perhaps move them again for good measure.
The skeletons of Srebrenica were therefore spread across mass graves up to 20 kilometres apart.
It dawned on us that the genocide had actually worked
In the mortuary we see half a jaw with five teeth left in a semi-translucent plastic bag. On the shelves above each set of remains are corresponding brown paper bags containing whatever clothes, wallets or other scraps of belongings may have belonged to that person.
Most of the mass graves are now thought to have been found, but Dragana tells us there are one, "perhaps two”, still to go. Now that funding has dried up, they may never be discovered.
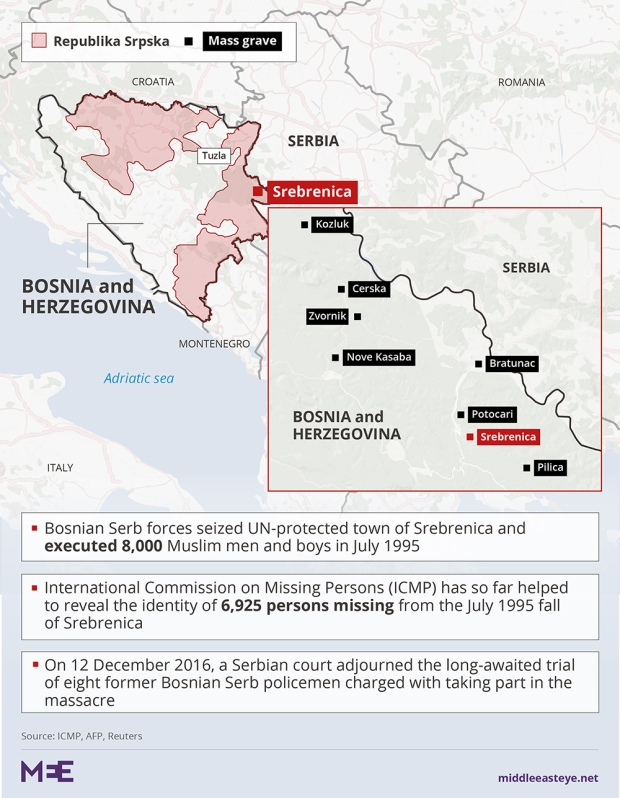
From Tuzla we drove towards Srebrenica, some 32 kilometres to the southeast, a haunting journey through villages that had been ethnically cleansed by Bosnian Serb forces and Serb militias during the war. Many Bosnian Muslims have left forever, while newly built churches mark Bosnian Serb possession of the territory.We also realised that that we were taking the same journey – only in the reverse direction – as the so-called "Death March" of 11 July 1995 when 10,000 Bosnian Muslims fled Srebrenica towards Tuzla after UN forces refused to protect them. Of those 10,000, some 7,000 were killed by Serbian forces.
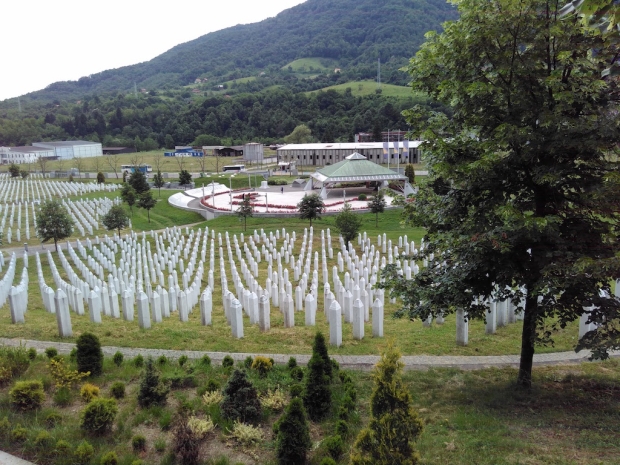
Eventually we reached Srebrenica, the site of the only genocide in Europe since the Second World War. The UN camp, which failed so terribly in its task to protect, has now been turned into a museum.
As at Tuzla, we were in for a very nasty shock. We had come to Srebrenica to learn about the events that led to the genocide. Chillingly, we learnt something else as well. It dawned on us that the genocide had actually worked.
Act of defiance
With most of the town's former Muslim residents dead or emigrated, Srebrenica is now controlled by Bosnian Serbs, the majority of whom refuse to accept that that genocide took place.
We met a survivor of the genocide who moved back to Srebrenica in an act of defiance, marrying a fellow survivor and having three children.
'They are being taught that the genocide never happened. You turn on the TV and it is like the war never ended'
"For a long time I thought we could make a life here," he told us, but now they want to move away. "Our first child is starting at the local school. They are being taught that the genocide never happened. You turn on the TV and it is like the war never ended."
Nedzad Avdic cannot doubt the genocide took place because his uncle and father, and many other male relatives, were also killed (only the bodies of his uncle and father have been found so far). His story is horrific: he himself survived after crawling away badly wounded from a mound of defenceless men who had been shot dead by the Serbs.
"We are still hoping the deniers will turn round finally and think about us and all the other mothers, but all they want to do is deny. If you turn the TV on all you can hear is them denying. We cry and cry and they still deny."
The mother told us that the first time she returned to her home, a neighbour threatened her. "He said he wanted to kill me, he chased us across the field cursing my dead children. Luckily my neighbour came. The police did nothing; this is Srpska now."
Srpska is the semi-autonomous northern and eastern region of Bosnia-Herzegovina which includes Srebrenica and borders Serbia. Since the war ended Srpska has been dominated by Bosnian Serbs.
Mejra Dzogaz told us that many of the same men she remembered carrying out the killings she now sees around the town, some holding offices at the local council or senior ranks in the local police force.
"I put so much sugar in my coffee every morning," she added, "but no matter how much I put in, it still tastes bitter."
Every year, the international community gathers in the cemetery at Srebrenica to commemorate the genocide.
The ceremony remains an important reminder that a genocide in Europe has happened since the Second World War, and that leaders should always be on their guard to avoid it happening again.
Like many Bosnian Serb nationalists, he still refuses to use the word genocide about the atrocities of July 1995 - even though Srebrenica is now regarded as the most well-documented and best evidenced war crime in history.
"I always said that what happened in Srebrenica was a terrible crime against the Bosnian population and that there were also terrible crimes against the Serbian population." Grjujicic has said, adding that "I leave it to competent institutions to qualify it."
Genocide denial
This is genocide denial. He ignores the fact that the International Court of Justice and the International Criminal Tribunal for the former Yugoslavia have both clearly ruled the killings "genocide".
A United Nations Security Council motion proposing to condemn the Srebrenica killings as genocide in 2015 was vetoed by Russia, Serbia and Republika Srpska's ally, but both the US Congress and the European Parliament have also passed resolutions calling the massacre a genocide.
The chairman of Remembering Srebrenica, Dr Waqar Azmi, said: "It is a cruel irony that the election of a new mayor of Srebrenica, who is a genocide denier, was made possible only because of the ethnic cleansing of its Muslim population." In Serbia itself, one 2015 poll showed 54 percent people do not question the crime's brutality, but an extraordinary 70 percent still deny it was "genocide". In November 2016, Serb legislators excluded Srebrenica from a new law forbidding genocide denial more widely.
Grujicic does not hold a minority view among political leaders in both Srpska and Serbia, and Bosnian Serbs who now live in the Republika Srpska.
Once 2015 poll showed that in Serbia, 54 percent of people do not question the crime’s brutality, but 70 percent still deny it was "genocide". In November 2016, Serb legislators excluded Srebrenica from a new law forbidding genocide denial more widely.
It is as if European Jews who survived the Holocaust had found themselves being ruled by the same criminals who denied the gas chambers existed, and who themselves had ordered the killings.
There is more than a little crossover between the anti-Muslim Chetnik Serb nationalist ideology, and anti-Jewish German Nazism.
"It was genetically deformed material that embraced Islam," Biljana Plavsic, the president of the Republika Srpska from July 1996 to November 1998 - regarded as the ideologue who provided the pseudo-intellectual underpinning for the genocide - once said.
She was later sent to The Hague and convicted of war crimes. "And now, of course, with each successive generation it simply becomes concentrated," she continued.
'It really hurts when people deny the murder of your family. It is just like a dagger to the heart, as if they never even existed'
- Lilian Black, chair of the Holocaust Survivors' Association
"It gets worse and worse. It simply expresses itself and dictates their style of thinking, which is rooted in their genes. And through the centuries, the genes degraded further."
Plavsic was a former Fulbright scholar and acclaimed biologist, lending a chilling air of scientific callousness to the "Greater Serbia" ideology of Slobodan Milosevic.
Lilian Black, the chair of the Holocaust Survivors' Association and director of the Holocaust Heritage and Learning Centre for the North, was also on the trip.
Black was shocked by the culture of denial in Srpska, and drew comparisons with her own family's experiences.
"It really hurts when people deny the murder of your family. It is just like a dagger to the heart, as if they never even existed. When we got the Nazi records from the International Tracing Service in Germany of our family’s persecution it was a truly cathartic experience," she said.
"It was like saying yes they were here and this is what happened to them. It doesn't change their fate, but it is somehow a means to helping us accept what happened."
Bosnian Serb nationalists' Trump links
Hungary was only a few hours drive from where we were standing, where Prime Miniser Viktor Orban has recently framed his own anti-refugee policy on distinctly religious grounds.
"Those arriving have been raised in another religion, and represent a radically different culture," Orban wrote in a commentary for Frankfurt Allgemeine Zeitung, a German newspaper.
"Most of them are not Christians, but Muslims."
In December, Slovakia banned public authorities from allowing Islam to be recognised as a religion.
One of the most disturbing aspects of our trip was the discovery of links between the new Trump administration and the genocide-denying tendency amongst Bosnian Serb nationalists.
Mayor Grujicic, who denies Srebrenica was a genocide, was invited to attend the prestigious National Prayer Breakfast event in Washington two weeks after Trump was inaugurated.
Grujicic said he hoped it would be "an opportunity to make contacts with some important persons, and I will try to do something useful for Srebrenica's residents".
Milorad Dodik, the president of the Republika Srpska, also received an invite to the Trump inauguration ceremony, extended by his transition team (before it was knocked down by a concerned US State Department).
'Nobody tries to argue that the Holocaust wasn't so bad because the allies also committed some war crimes'
Dodik has called Srebrenica "the greatest deception of the 20th century".
Our trip, which was organised by the British charity Remembering Srebrenica, was hosted by Bosnian Muslims who had fought or suffered greatly during the war.
Systematic atrocities
None denied that crimes by Muslim fighters had also taken place against Serbs, but there was an important and qualitative difference between the two.
According to Azmi, who is now working on plans for a Srebrenica memorial centre in Britain, "Nobody tries to argue that the Holocaust wasn't so bad because the allies also committed some war crimes.
"Bosniak [Bosnian Muslim] war crimes were sporadic and isolated, and Bosniaks were fighting for a multi-ethnic, multi-religious society. Serb war crimes were organised and systematic, and Serbs were fighting for a mono-ethnic 'Greater Serbia'."
It is clear when you visit Srebrenica that what happened there in July 1995 was by far the greatest atrocity of the Yugoslav conflict.
It was also not an incident that can be understood simply by tracing out the mechanics of what took place minute by minute, hour by hour, on those particular days.
Srebrenica was the culmination of years of increasingly explicit anti-Muslim hate speech in the Serbian media, and in the speeches and rhetoric of figures like Slobodan Milosevic, and the Bosnian Serb political and military leaders, Radovan Karadzic and Ratko Mladic.
Milosevic, who was overthrown in 2000, was extradited to The Hague and accused of genocide and other war crimes but died before his trial concluded. Karadzic and Mladic were both captured in Serbia, in 2008 and 2011, respectively, with the former found guilty of genocide and sentenced to 40 years in prison. Mladic's trial, in which he faces two indicted for two counts of genocide, is ongoing.
Yet the strength of their anti-Muslim ideology clearly lives on in Serbia and Republika Srpska. It is this that made us wonder - could a Srebrenica-style genocide in Europe happen again?
Alastair Sloan focuses on injustice and oppression in the West, Russia and the Middle East. He contributes regularly to The Guardian, Al Jazeera and Middle East Eye. Follow Alastair's work at www.unequalmeasures.com
Peter Oborne was named freelancer of the year 2016 by the Online Media Awards for an article he wrote for Middle East Eye. He was British Press Awards Columnist of the Year 2013. He resigned as chief political columnist of the Daily Telegraph in 2015. His books include The Triumph of the Political Class, The Rise of Political Lying, and Why the West is Wrong about Nuclear Iran.
The views expressed in this article belong to the author and do not necessarily reflect the editorial policy of Middle East Eye.
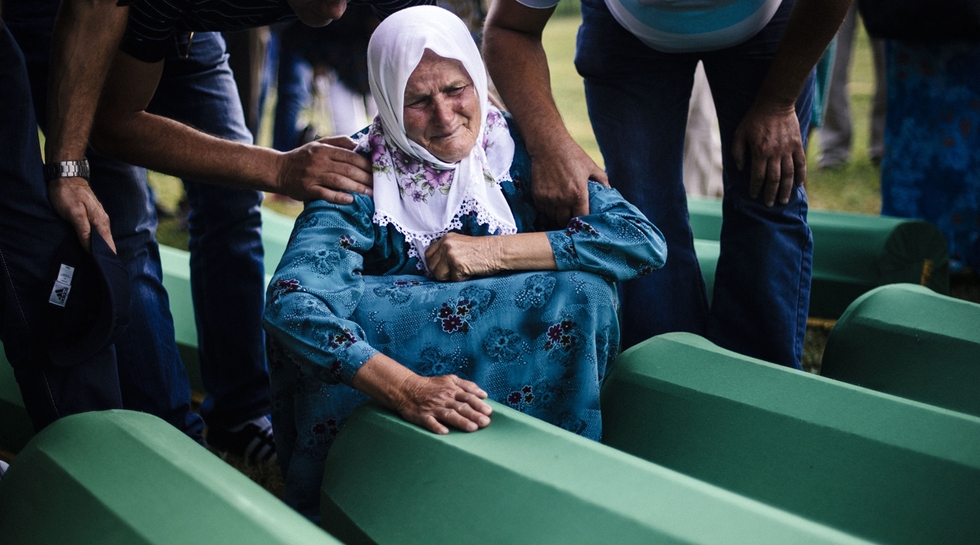
Photo: A Bosnian woman mourns over a coffin of a relative at the Potocari Memorial Center near the eastern Bosnian town of Srebrenica on 10 July 2015 where 136 bodies found in mass grave sites in eastern Bosnia will be reburied on 20th anniversary of the Srebrenica massacre. (AFP)
This article is available in French on Middle East Eye French edition.
Middle East Eye propose une couverture et une analyse indépendantes et incomparables du Moyen-Orient, de l’Afrique du Nord et d’autres régions du monde. Pour en savoir plus sur la reprise de ce contenu et les frais qui s’appliquent, veuillez remplir ce formulaire [en anglais]. Pour en savoir plus sur MEE, cliquez ici [en anglais].